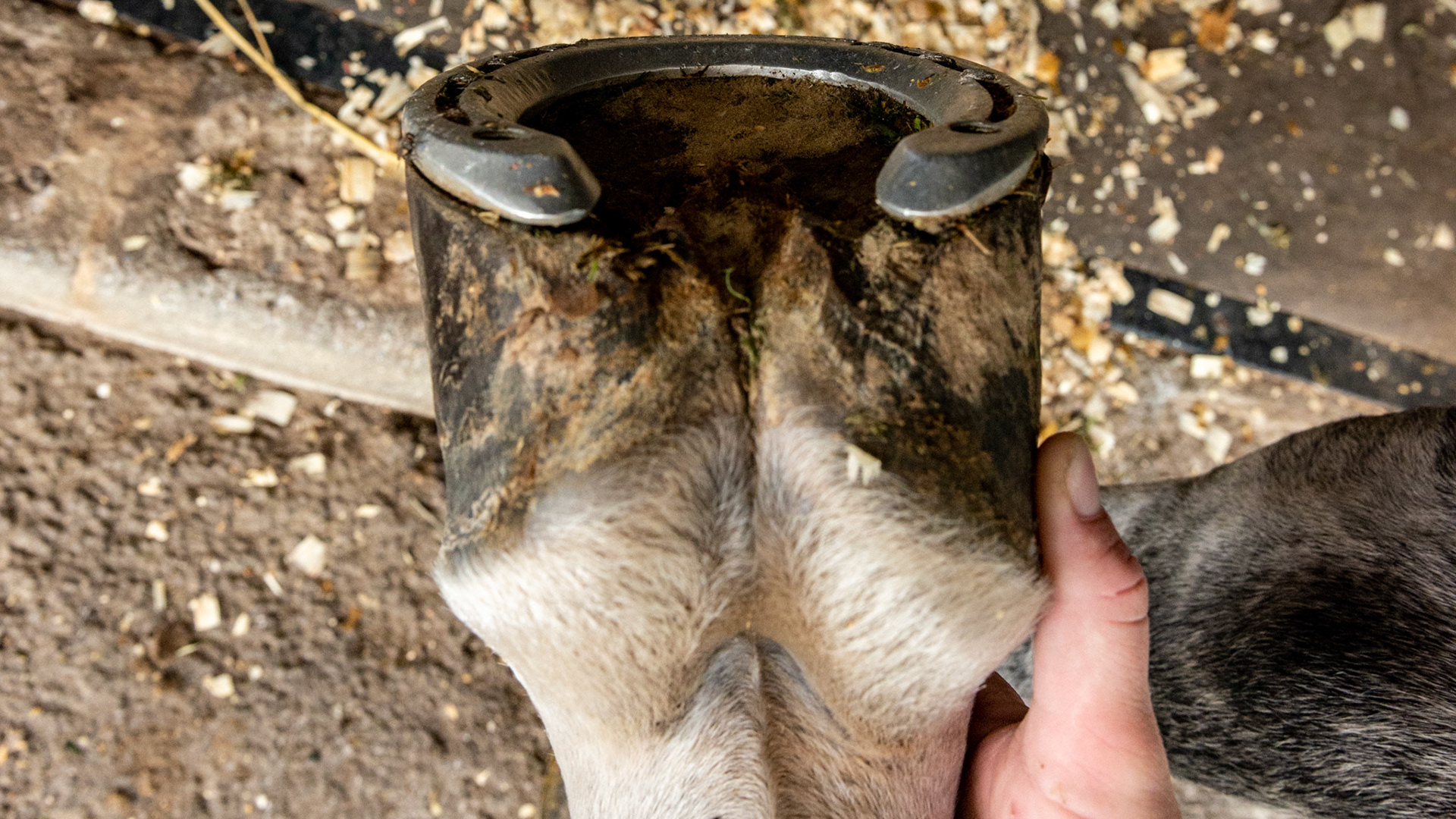
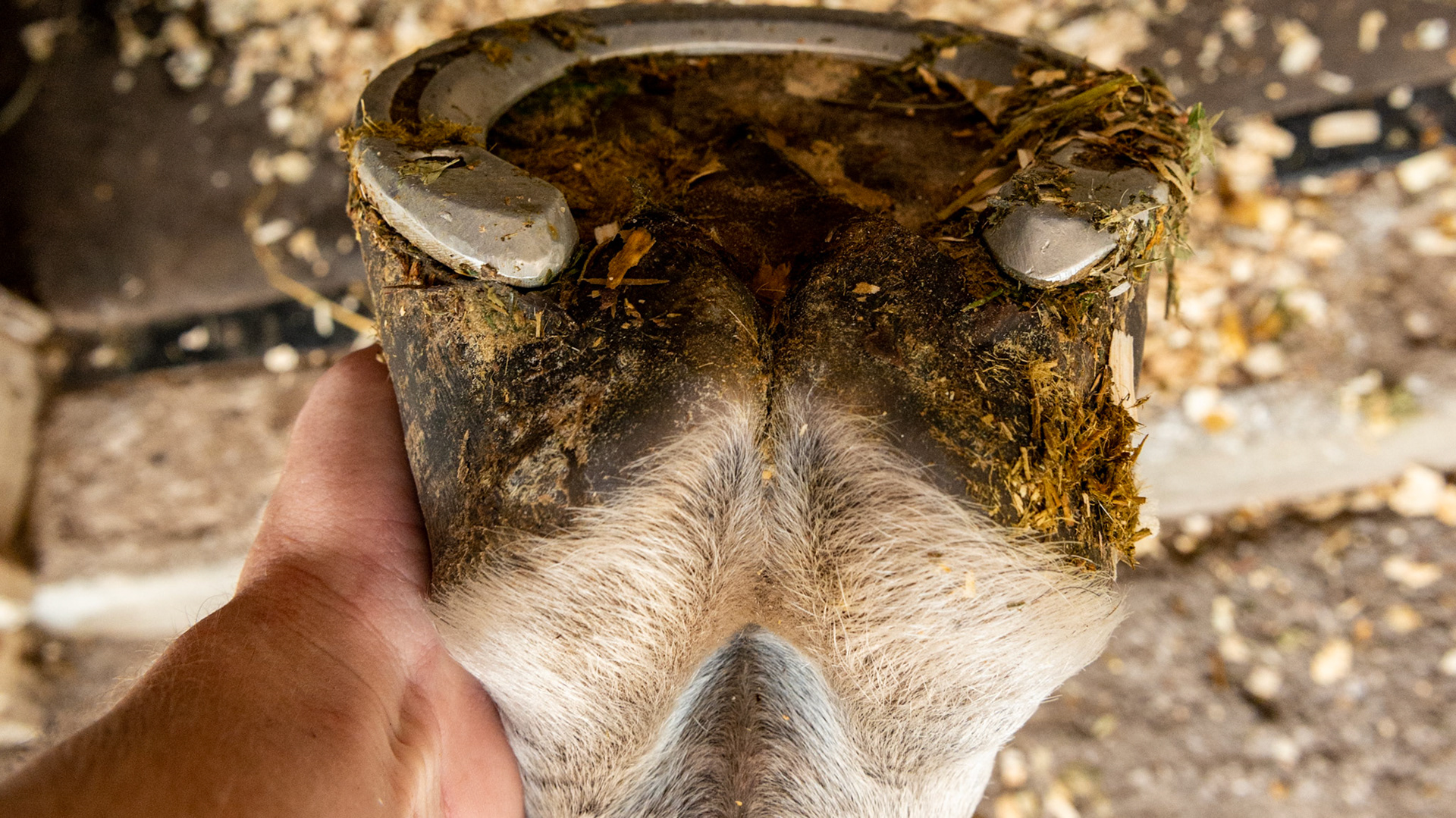
Horse A - LF and RF - Uneven (asymmetric) heels - medial heel bulbs not shaped the same, different length from coronary to ground, especially on the left fore with a higher median sulcus caused by shearing due to one heel landing before the other. Also the medial wall of the LF is dishing and heels of both hooves are under-run.

Horse B - One horse with 2 completely different front hooves. The RF has vertical side walls, a dished in toe, elevated coronary band on the inside, and long and uneven heels.

Horse B - One horse with 2 completely different front hooves. This is the left hoof that appears more normal with a balanced shape and even coronary band, however, the hoof pastern axis is slightly broken and the heels are underslung (not seen in this image).

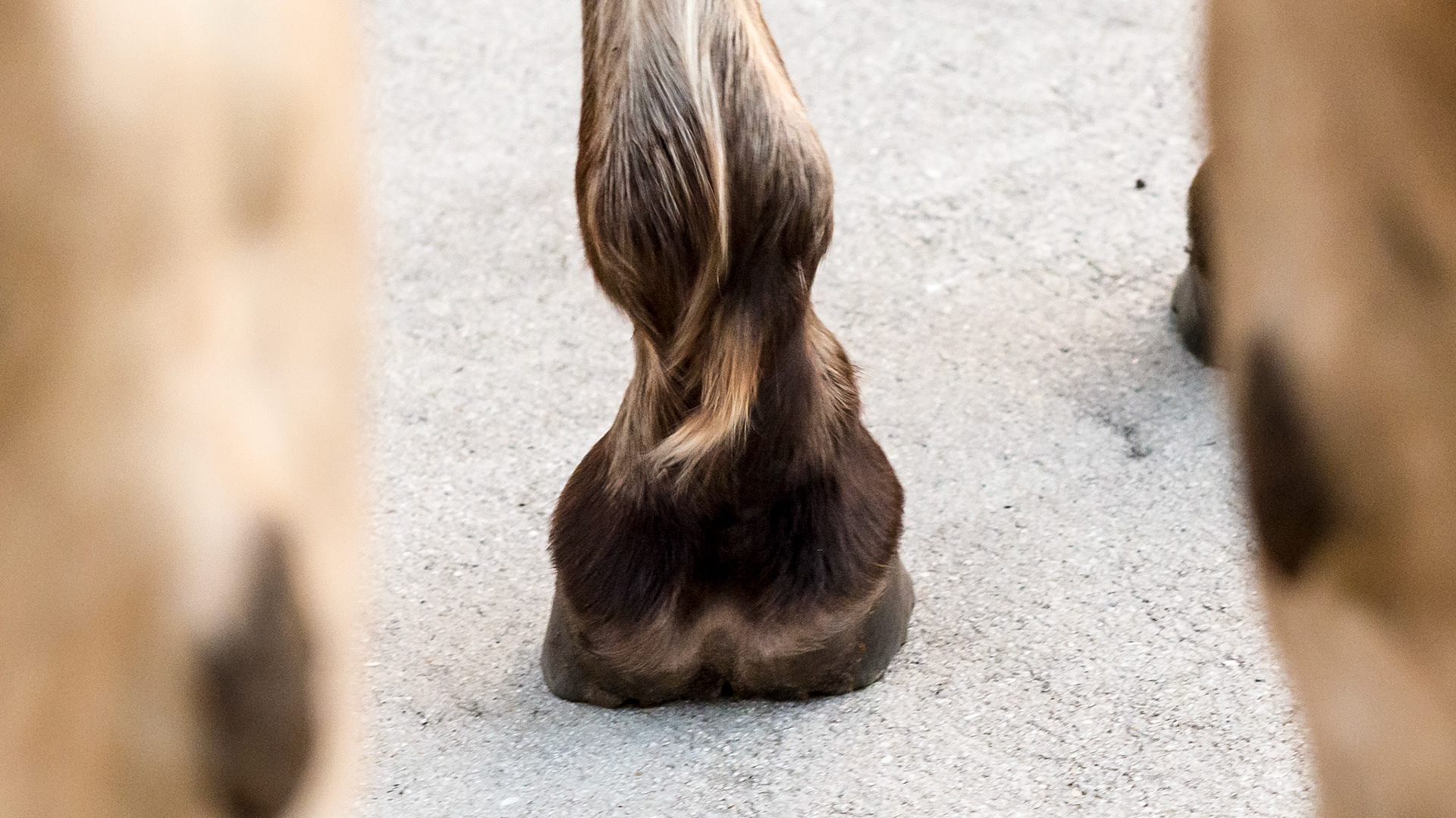
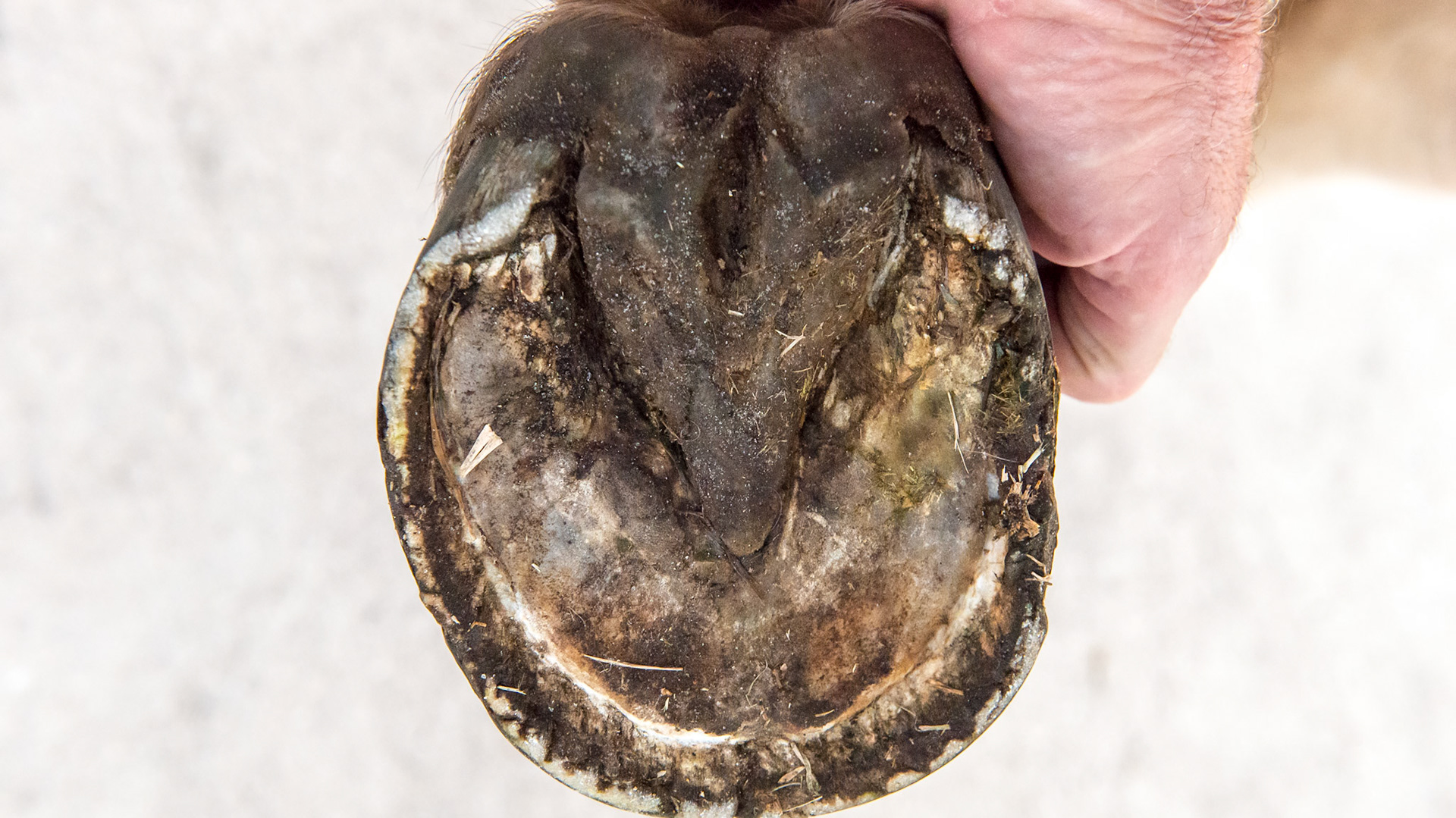
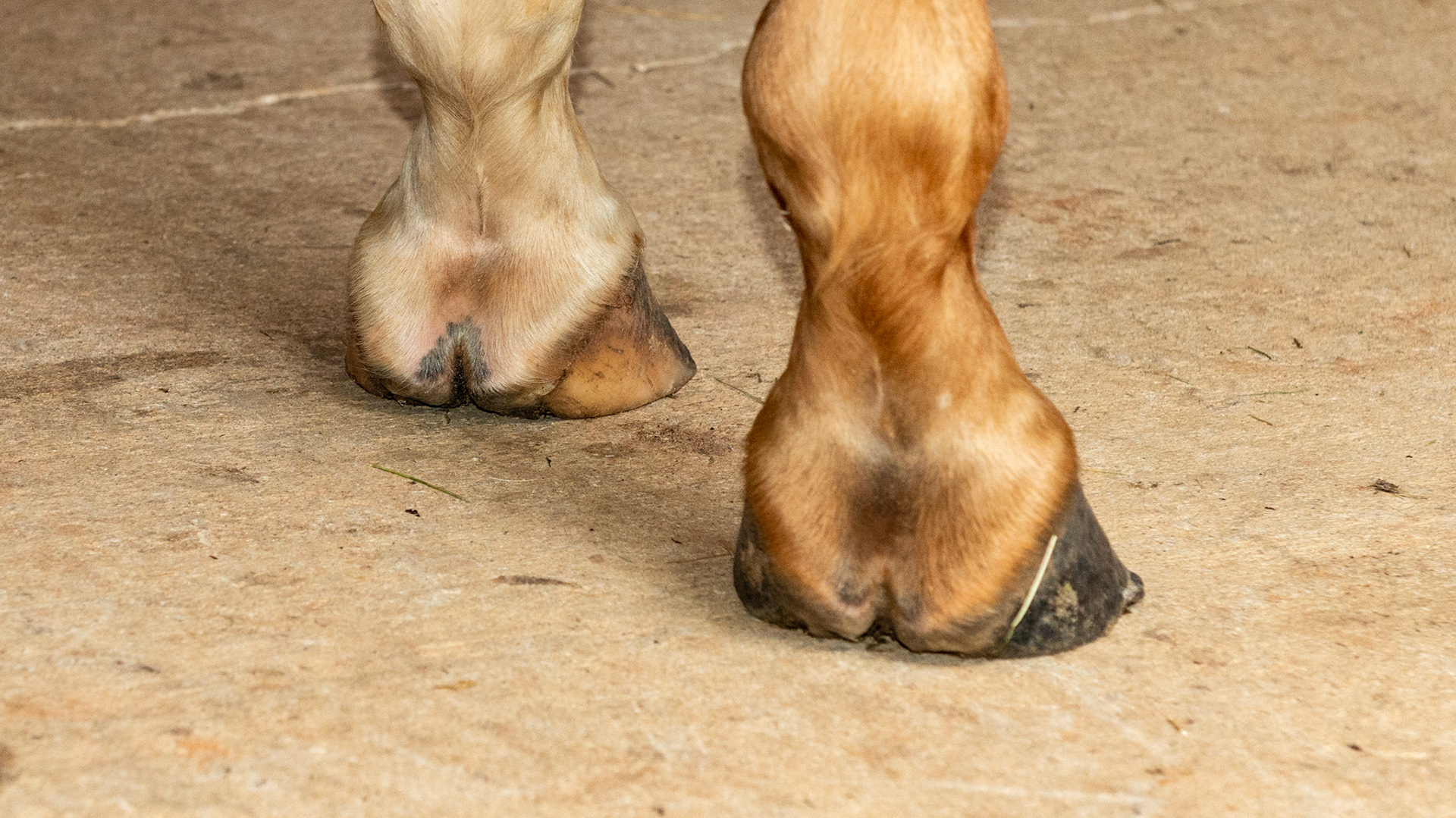
Horse J - The LF hoof of this horse has an asymmetric hoof and an offset pastern entering the hoof.

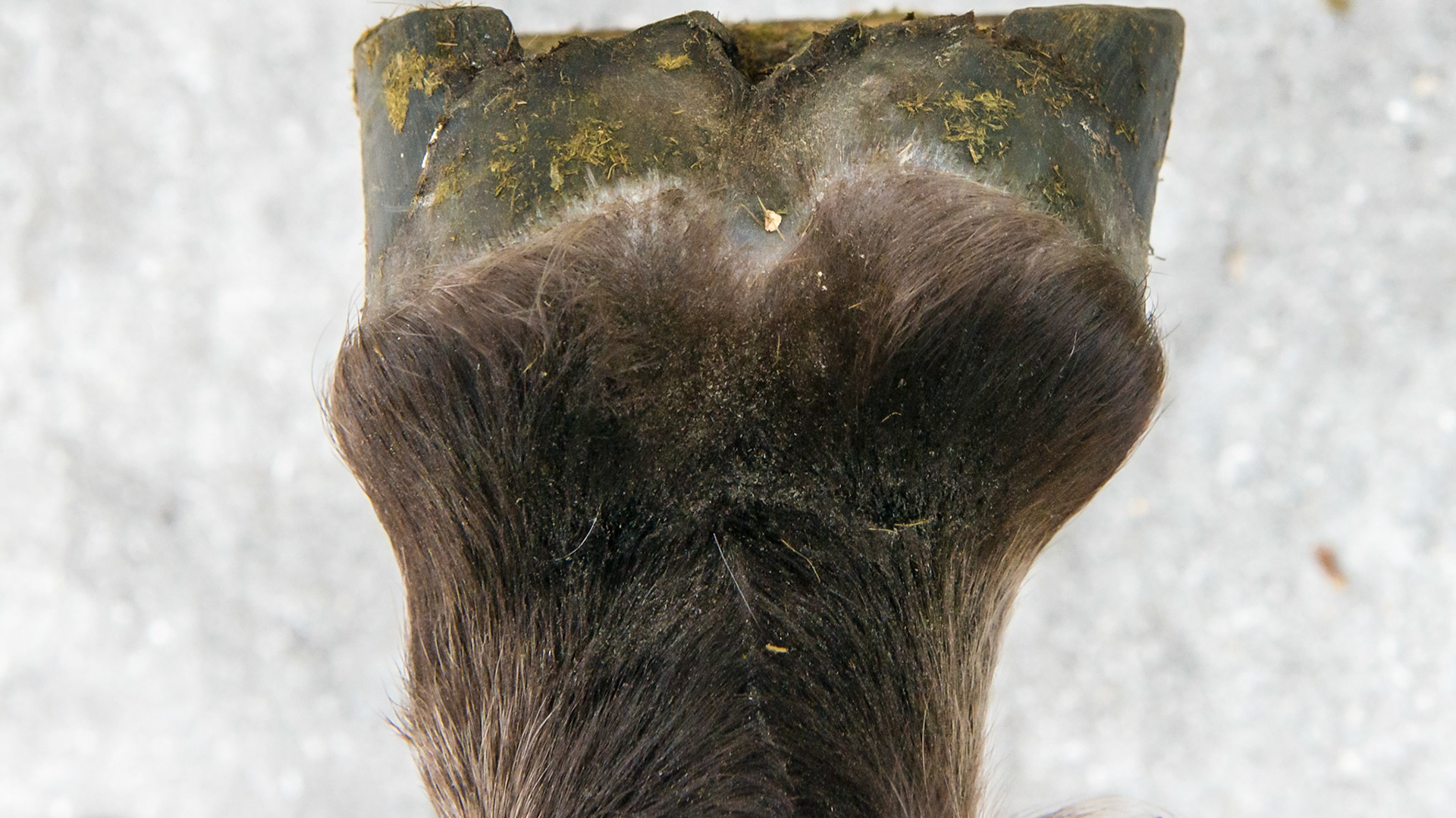
Horse J - The LF hoof of this horse has an asymmetric hoof and an offset pastern entering the hoof. This rear view shows the uneven heels and the lateral deviation of both heels.

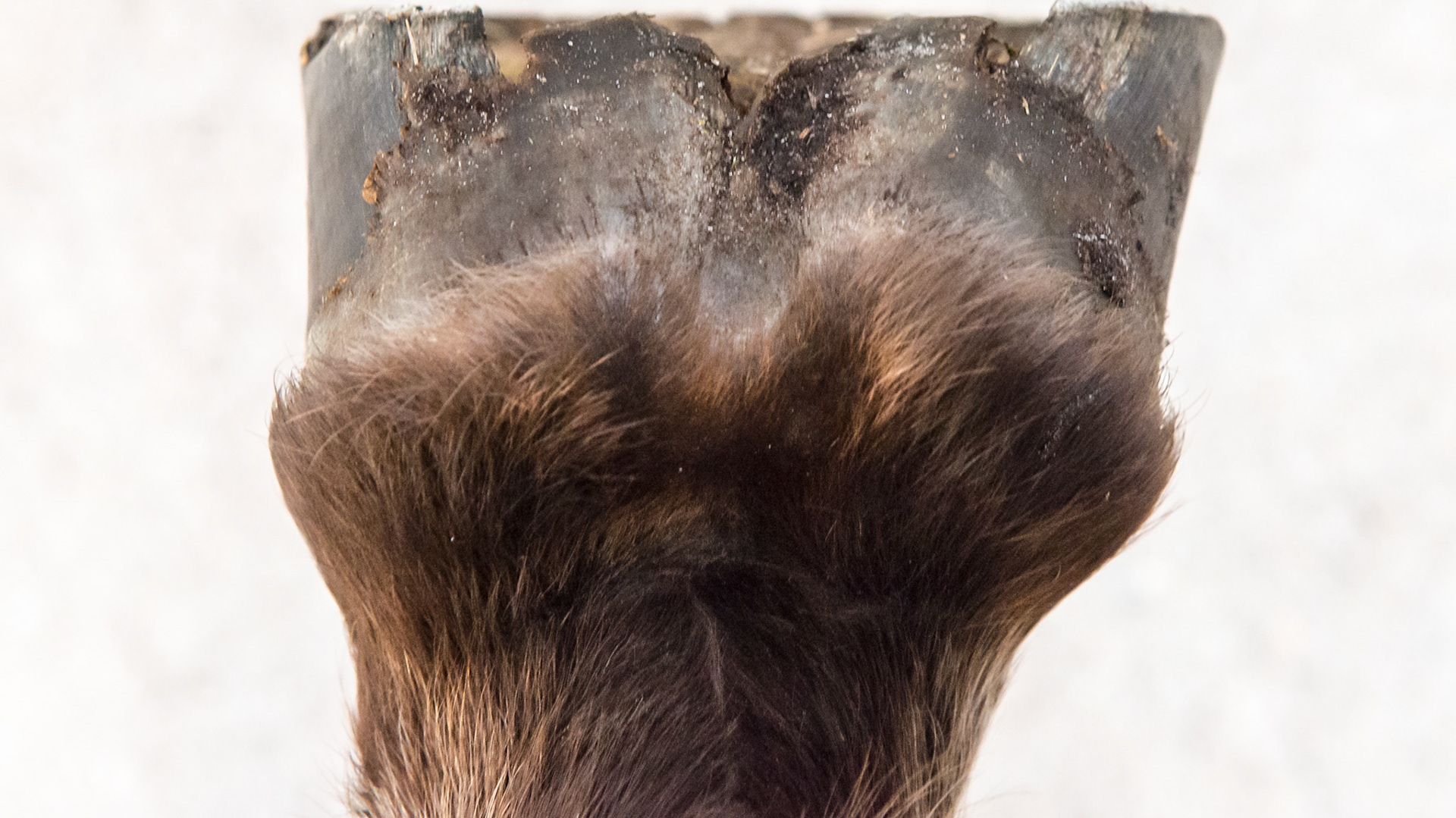
Horse J - The LF hoof of this horse has an asymmetric hoof and an offset pastern entering the hoof. This view shows the vertical medial wall, the higher medial heel and the horizontal splay of the lateral heel and hoof wall. This geometry is a result of the medial side landing first causing an upright wall and elevated heel and the lateral side landing last with the force vectors being more horizontal and moving the wall outward.

Horse J - The LF hoof of this horse has an asymmetric hoof and an offset pastern entering the hoof. This view shows the vertical medial wall and the higher medial heel next to my hand as well as the broken hoof wall from the increased downward load of the horse. The sole is not divided equally but the medial side has less area than the lateral when a line is drawn from the toe to the point of the frog.

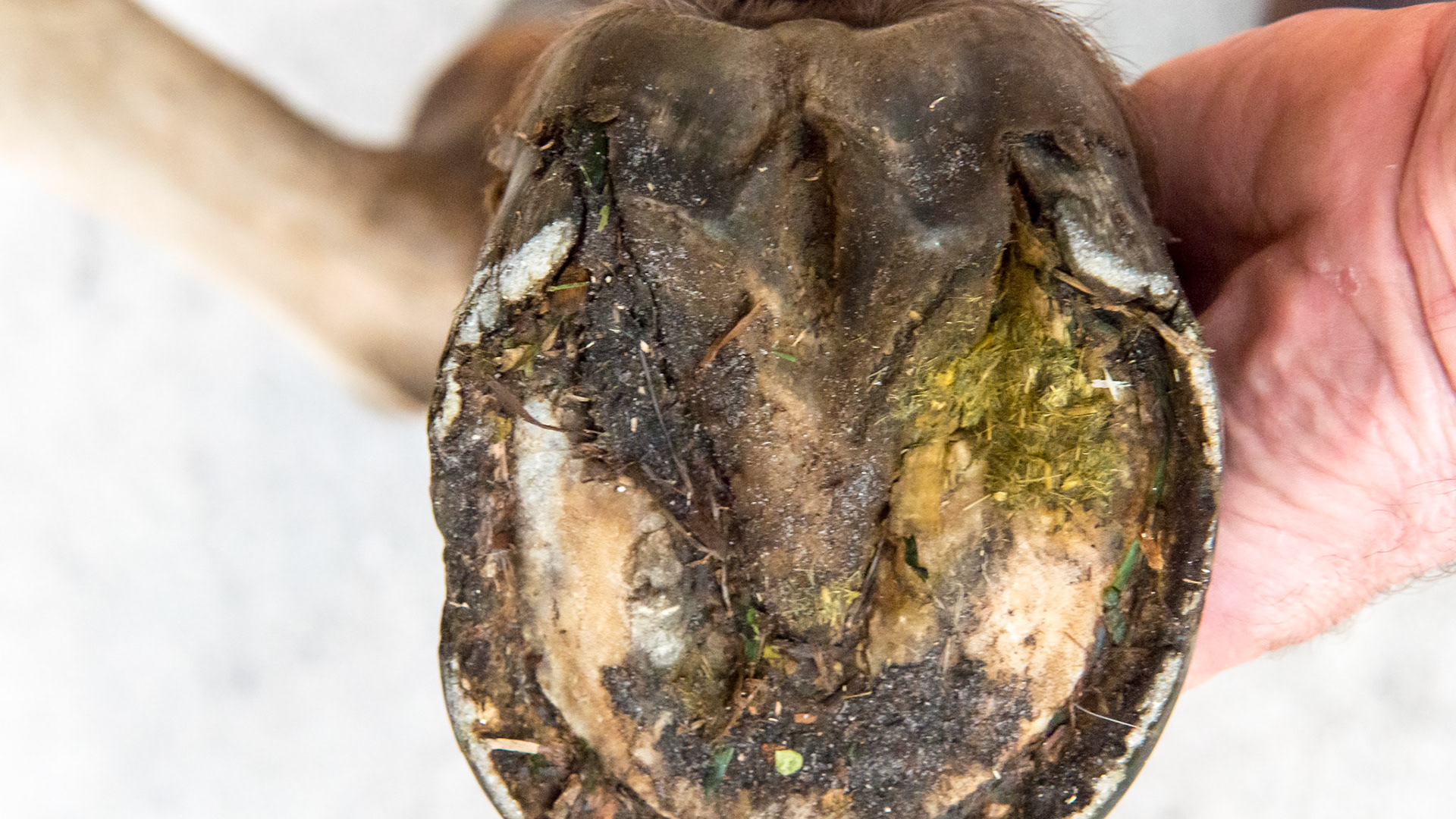
Horse J - the RF hoof also showing a sheared hoof with a vertical medial wall and a laterally splayed lateral wall. These are not as obvious when viewing from the front because the LF is more deviated.

Horse J - the RF hoof also showing the vertical medial wall and the higher medial heel away from my hand as well as the broken hoof wall from the increased downward load of the horse. The sole is not divided equally but the medial side has less area than the lateral when a line is drawn from the toe to the point of the frog.

Horse J - the day after trimming (2 days after the 1st images). The medial heel (left side) is taller while the lateral heel and quarter are splayed out. From this image it is clear the horizontal component of the vector analysis is forcing the hoof to move laterally (to the right in this image). There is a video of the movement of these limbs. 5 years later: the hooves have been supplemented with protein and trimmed correctly and the hooves are normal (images to follow).